What is an eSIM? Everything you need to know

An eSIM is a SIM card that lets you activate mobile service without swapping any physical card or visiting a store.
Most recent iPhones and Android devices support eSIM. Carriers now provide digital SIM card activation, so you can add a plan, switch providers, or set up a travel data option in minutes.
This guide explains what an eSIM is, how it works, how it differs from a physical SIM, and what changes when you switch. You’ll also learn how to set one up, how to solve common issues, and how to stay secure on public networks.
What is an eSIM?
An eSIM is a SIM card that’s built right into your device. It performs the same job as a physical SIM by identifying you on the network, but it’s integrated into the hardware instead of sitting in a tray.
It can be activated digitally; your carrier provides the details your device needs, and your phone adds the plan through its settings. With no card to handle, activation and updates are entirely software‑based.
Because everything is managed on the device, you update or replace your mobile plan through your carrier or your phone’s menus. As long as your device and carrier support eSIM, setup is typically quick and reliable.
How does an eSIM work?
An eSIM is a tiny secure chip built into your phone. It stores your mobile plan as a digital SIM profile instead of on a removable card. Instead of sliding in a new SIM every time you change plans, your phone just loads a new profile onto that chip.
This is handled via remote SIM provisioning, which is the system your carrier uses to install or update your mobile plan on your phone over the internet without anyone touching the device or a physical card.
Activation usually looks like this:
- Your carrier gives you activation details: Often a QR code, a short activation code, or instructions in their app.
- Your phone connects securely to the carrier online: This enables you to download your eSIM profile (the “digital SIM card”).
- The profile is written to the eSIM chip: Your number is activated, and the phone starts registering on the mobile network.
 Once that’s done, the eSIM works just like a physical SIM for calls, texts, and data. However, unlike with a physical SIM, most modern phones can store several eSIM profiles simultaneously, and you can switch between them in your Settings. This is much more convenient than having to swap physical SIM cards or use multiple phones for different purposes.
Once that’s done, the eSIM works just like a physical SIM for calls, texts, and data. However, unlike with a physical SIM, most modern phones can store several eSIM profiles simultaneously, and you can switch between them in your Settings. This is much more convenient than having to swap physical SIM cards or use multiple phones for different purposes.
eSIM vs. physical SIM: Key differences
| Feature | eSIM | Physical SIM |
| Format | Built into the device | Removable card |
| Activation | Digital setup through QR code, app, or carrier settings | Insert card into tray and wait for network to activate |
| Switching carriers | Change plans through software | Replace the SIM card with a new one |
| Number of profiles | Can store multiple profiles on compatible devices | Usually holds only one plan |
| Security | Can’t be removed if device is lost or stolen (but can still be remotely reprogrammed) | Can be physically removed, swapped, or stolen |
| Durability | No risk of losing or damaging a card | Card and tray can be damaged or misplaced |
| Travel convenience | Easily activate local plans abroad | Must buy and insert a local SIM |
| Device swapping | Can be moved to a new device, but usually requires carrier activation or setup | Can move the card to another phone instantly |
Advantages of eSIM
- Multiple numbers on one device: An eSIM lets your device hold more than one mobile plan. You can keep personal, work, or travel numbers and switch between them in your settings.
- Simple carrier switching: Changing carriers is simpler because activation happens in software. Your new provider sends a QR code or activation link, and your phone downloads the plan. The device handles the rest, and you can move between carriers without waiting for a physical card to arrive.
- Enhanced security features: Since a virtual SIM can't be removed, there’s no risk of someone popping it out and using it on another device. It doesn’t prevent account-based attacks, but it does remove that physical point of failure.
- No physical damage risk: There’s no tiny card to misplace or tray to bend. Everything happens in the software, so you’re not relying on a fragile piece of plastic to keep your phone connected.
- Suitable for travel and remote work: You can pick up a local or travel data plan in minutes, often before you even leave the airport Wi-Fi.
Disadvantages of eSIM
- Not all devices support it: Newer phones, tablets, and wearables usually have eSIM built in, but many older or budget models don’t.
- Switching phones can be tricky: Unlike swapping a physical SIM, moving an eSIM may mean redownloading the eSIM profile to the new device or even reissuing the eSIM. That said, newer phone models usually provide the option to transfer the eSIM wirelessly.
- Requires internet for activation: Your device has to download the eSIM profile, so you’ll need an internet connection to get started. Once it’s installed, it runs normally without internet.
- Limited availability in some regions: eSIMs are becoming more popular, but they're not available everywhere. Some carriers still stick to physical SIMs, and travel-friendly eSIM options vary by country.
How to set up an eSIM
Setting up an eSIM is simple. The details vary by device model and carrier, but the core steps are pretty similar whatever your device.
Before you set up an eSIM on any phone, check a few basics:
- Make sure your phone supports eSIM: Most recent iPhones and many Android phones do, but it’s worth confirming in the specs or settings.
- Confirm your carrier has enabled eSIM for your plan: Some providers only support it on certain plans or in certain countries.
- Connect to the internet: You’ll need it to download and activate the eSIM profile.
Set up eSIM on iPhone
Most recent iPhones support eSIM; Apple lists eSIM support starting from iPhone XS, iPhone XS Max, and iPhone XR. In fact, some models, such as the iPhone 14 sold in the U.S., no longer include a physical SIM tray.
You can configure the eSIM on your iPhone during initial setup or at any time afterwards. Whether your carrier has already assigned the eSIM or you’re transferring from another iPhone, this setup process guides you through activation.
Note: The exact menus you see can vary by iOS version, carrier, and region. The screenshots in this guide are from an iPhone 15 running iOS 26.
- Connect the iPhone to Wi-Fi and open Settings. Tap Cellular (Mobile Service on some models).
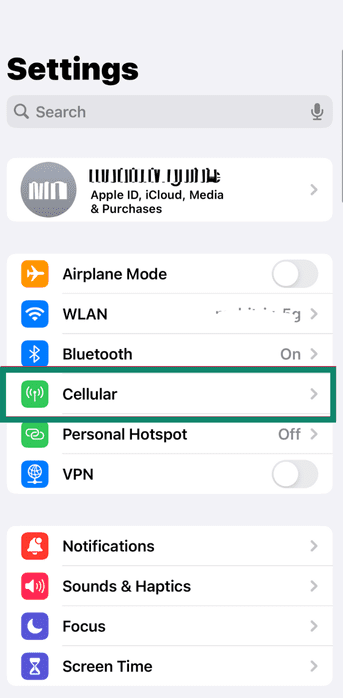
- Tap Set up mobile data, Add eSIM, or Add Mobile Plan (the exact wording depends on your version).
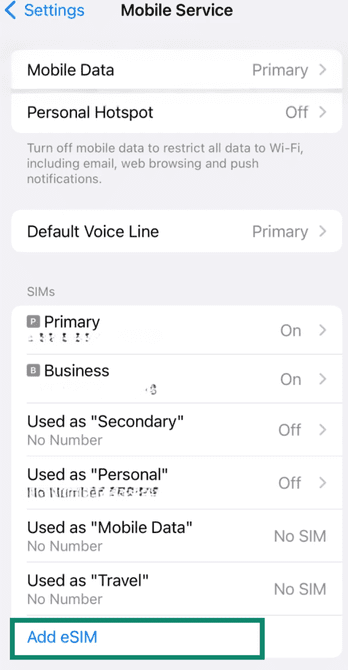
- Here you may see different ways to proceed depending on your carrier and whether you’re setting up the iPhone for the first time or adding an eSIM later. Here’s what to do:
- Choose Transfer From Nearby iPhone if your current number is already active on another iPhone that’s next to you.
- Choose Use QR Code if your carrier has provided you with a QR code or activation details. If your iPhone is already set up, you may be prompted to scan the QR code first and then return to Settings to confirm and add the plan.
- Choose Transfer From Android if you see the option (only on iOS 26 and up). Note that this option only appears with supported carriers and compatible devices. If you don’t see it, you’ll usually need to activate it via eSIM Carrier Activation or a QR code from your carrier.
- If your carrier has already assigned you an eSIM (eSIM Carrier Activation), you may see a Carrier Cellular Plan Ready to Be Installed notification. Tap it, then tap Continue to install the plan.
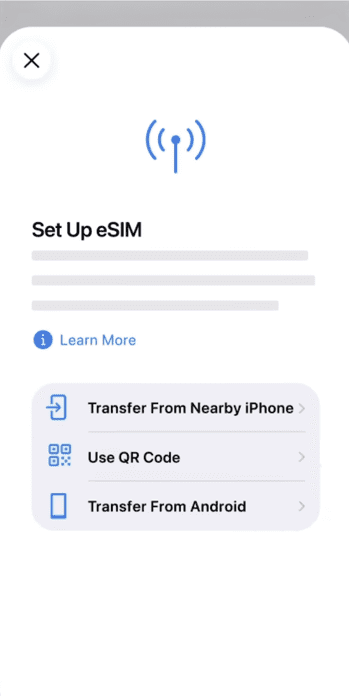
- Follow the instructions on the screen to download the eSIM plan or complete the carrier-assisted activation. For this guide, we used the QR code method.
- If your iPhone is already set up, open the Camera app and scan the QR code, then tap the Cellular Plan Detected notification to continue.
- On iOS 17.4 or later, if the QR code is shown in an email or browser, you may be able to press and hold it and tap Add eSIM.

- If you don’t have a QR code, then choose Enter Details Manually at the bottom of the screen and provide the Activation Code to continue.
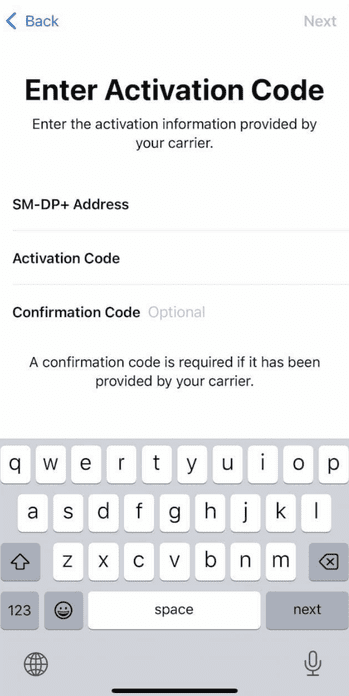
- Once added, you’ll see the Cellular Setup Complete screen, so press Continue to proceed.
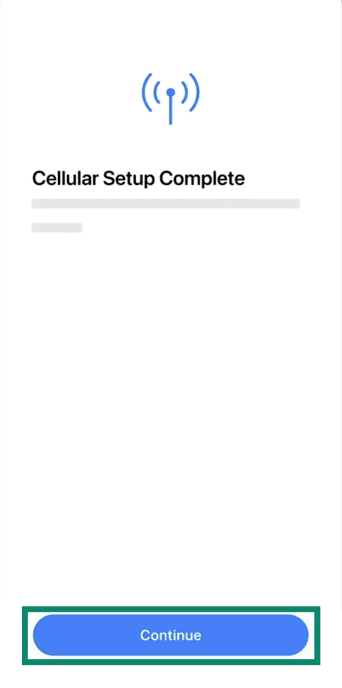
This process varies slightly by carrier and region, so the steps may differ.
Other ways to activate an eSIM on iPhone
Depending on your carrier, you might also be able to activate an eSIM in these ways:
- Carrier app: Some carriers let you activate an eSIM in their app. Download your carrier’s app from the App Store and follow the in-app setup steps.
- Carrier link: Your carrier might send an activation link instead of a QR code. On iOS 17.4 or later, open the link and follow the prompts to add the eSIM.
Pro tip: iPhones that support eSIM can use a travel eSIM that you add before your trip. When you arrive at your destination, you may see a prompt to Turn On Travel eSIM. At this step, Apple lets you pick Travel eSIM Only or Travel eSIM and Current eSIM. If you keep both lines active, the travel eSIM is used for data, while your home eSIM can still receive calls and texts and may still incur roaming fees.
Set up eSIM on Android
Android phones support eSIMs across many brands, but the steps may vary slightly depending on your device and Android version. These steps follow the layout on recent Google Pixel phones.
- Open Settings and tap Network & internet.
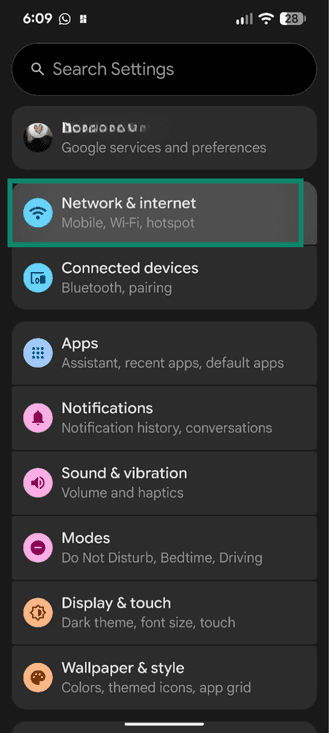
- Tap SIMs.
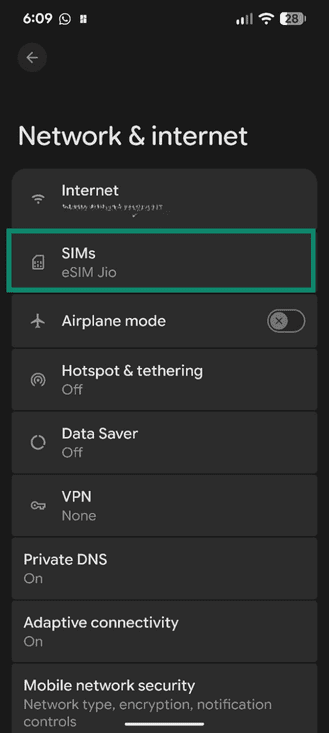
- Tap Add SIM.
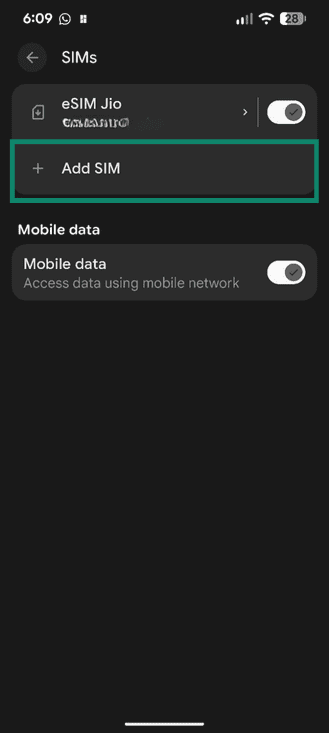
- Tap Set up an eSIM.

- You’ll be asked to Scan QR code from carrier using the camera. Scan the QR code if you have one; if you don’t, you can select Try these troubleshooting tips.
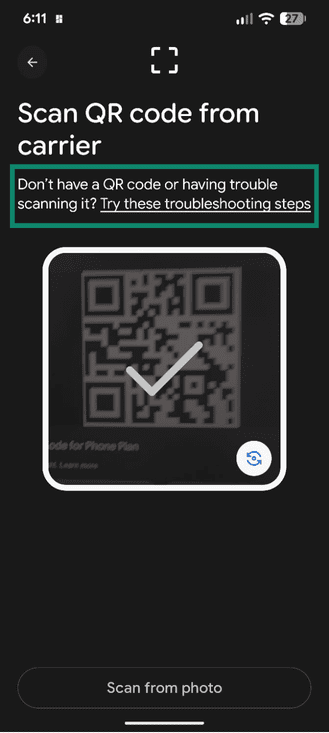
- Choose to Enter activation code if you’re using this option instead of a QR code.
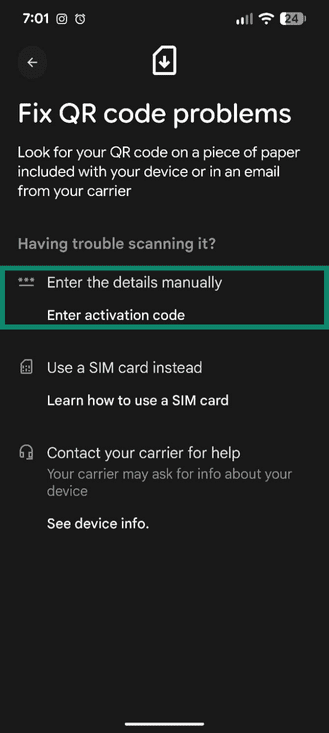
- Follow the on-screen instructions to download the virtual SIM profile from your carrier or to enter activation details. Once done, the plan should appear as active.
On Samsung Galaxy phones, you can go to Settings > Connections > SIM manager (sometimes labeled SIM card manager) when you need to add or manage an eSIM. On most other Android phones, you’ll see similar options in your Settings under Network & internet or Mobile network.
Once the setup is complete, your phone confirms that the line is active. You can then set your preferred SIM for calls, messages, and mobile data in the SIM manager or Mobile network settings screen you just used.
Troubleshooting common eSIM issues
Most virtual SIM setups work without much effort, but things can go wrong during activation or when you’re switching plans or phones. Here’s how to tackle some common problems.
eSIM not activating
Activation hiccups usually come down to three things: the carrier didn’t assign the plan correctly, your phone can’t reach the activation server, or your device needs a software update.
Start with the basics: make sure you have a stable internet connection and restart your phone. If your carrier gave you a QR code, scan it again to pull in fresh activation details. Some devices need the latest software version before they’ll accept an eSIM, so check for updates if it still won’t load.
eSIM not detected by device
If your phone can’t “see” the eSIM, the profile probably didn’t download correctly, the carrier info is incomplete, or the device simply doesn’t support eSIM.
Double-check that your phone model offers eSIM and that your carrier supports it where you live. Restart the device, then try adding the eSIM again through your settings. Carriers may use different activation flows, so check you’re following the correct method, whether it's QR code, app prompt, or manual download.
Cellular connectivity issues
Sometimes the eSIM activates, but the phone still refuses to connect. That usually points to missing carrier settings, incorrect mobile data configuration, or weak local coverage.
Flip the Airplane mode on and off to refresh your connection. In your Settings, confirm the right SIM is selected as the active data line. If you’re traveling, make sure your plan actually includes roaming or international data.
Resetting network settings
If nothing else works, a network settings reset can wipe saved Wi-Fi networks, carrier profiles, and APN settings, which gives your phone a clean slate.
On iPhone:
- Open Settings and tap on General, then Transfer or Reset iPhone.
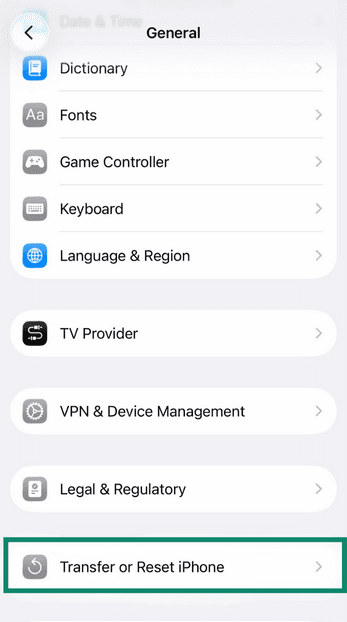
- Tap Reset and then select Reset Network Settings.
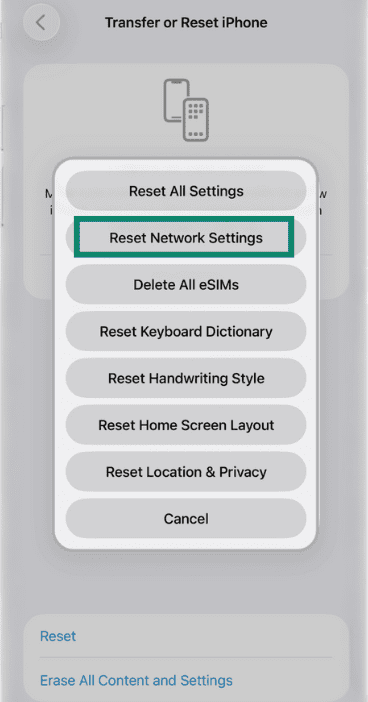
Wait for the iPhone or iPad to reboot before you try to install the eSIM again.
On Android:
- Open Settings and tap System. On Samsung devices, the reset option could also be found under the General Management option.
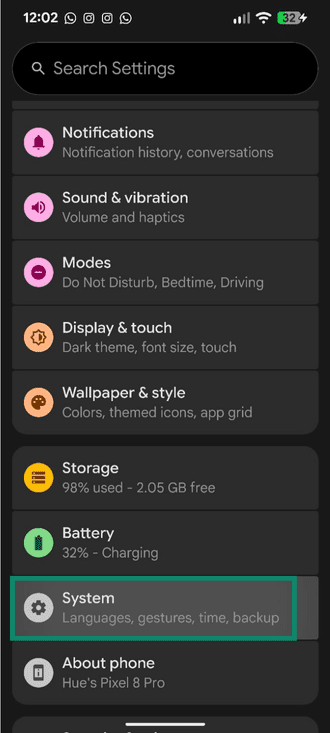
- Tap Reset options.
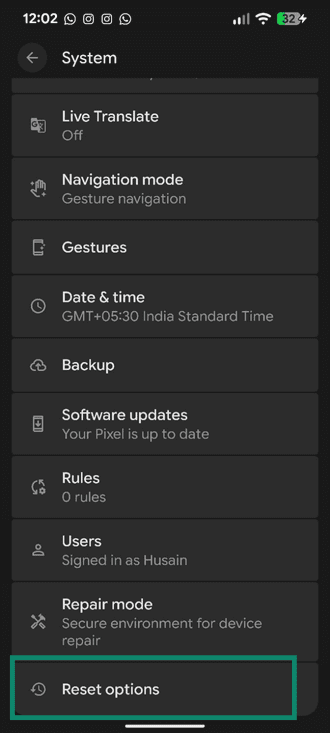
- Select Reset Mobile Network Settings.
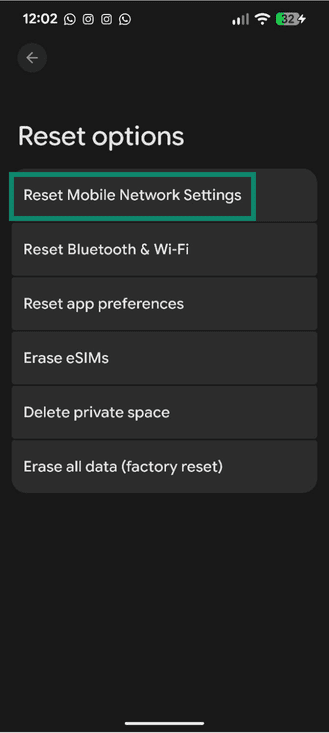
- If you see an Erase eSIMs option, only select it if you want to remove the eSIM profiles from the phone. You may need your carrier to reinstall them afterwards. Tap Reset settings to confirm.
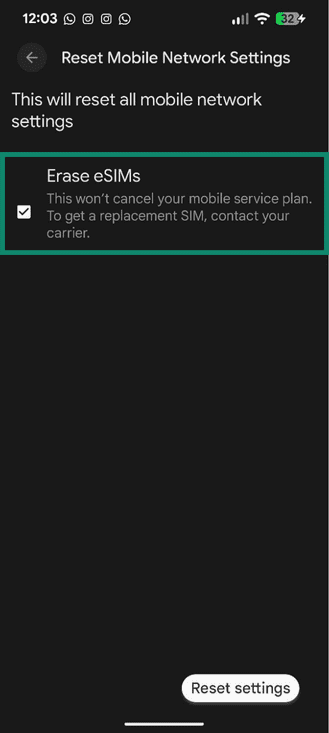
After the reset, restart your phone and try activating or re-adding the eSIM. These steps could vary slightly depending on your Android model and the software version installed.
Which phones and carriers support eSIM?
Even if your phone technically supports eSIM, your carrier might not offer it in your country yet. In some markets, operators roll out eSIM more slowly because of local rules. Availability can also vary because some regions require identity checks for mobile service, and these rules affect how both physical SIMs and eSIMs are issued.
Phones that support eSIM
Most modern smartphones in the U.S. support eSIM. Apple, Google, and Samsung all include eSIM on their flagship devices, and the newest U.S.-sold iPhones and Google Pixels no longer include a physical SIM tray.
Apple iPhones (U.S.)
Every iPhone from the iPhone XS, XS Max, and XR supports eSIM. All iPhone 14, iPhone 15, and iPhone 16 models sold in the U.S. are eSIM-only and don’t have a SIM tray.
Google Pixel
Google Pixel phones started supporting eSIM with the Pixel 2 on Google Fi, with wider, mainstream eSIM support arriving on the Pixel 3. Recent Pixel devices, including Pixel 7, 8, and Pro models, support multiple eSIM profiles, and U.S.-sold Pixel 10 models are eSIM-only.
Samsung Galaxy
Samsung introduced eSIM on the Galaxy S20 series and continues support on newer Galaxy S, Z Flip, and Z Fold models sold in the U.S.
Motorola, OnePlus, and others
Select Motorola models, including the latest Edge and Moto G models, certain OnePlus models (such as the OnePlus 11), and some Sony and Huawei devices sold internationally also support eSIM. Availability varies by carrier.
Carriers that support eSIM
All major U.S. carriers support eSIM activation for most current iPhone, Pixel, and Samsung devices. You can activate plans through QR codes, carrier apps, or built-in setup prompts.
Major carriers
- AT&T
- Verizon
- T-Mobile
U.S. MVNOs with eSIM support
Many U.S. mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs), which are essentially carrier resellers that run on the big networks, now support eSIM activation, including:
- Mint Mobile
- Google Fi
- Visible
- Metro by T-Mobile
- Cricket Wireless
Other devices that are eSIM-compatible
eSIM isn’t limited to phones. Many tablets, wearables, and laptops also support eSIM plans.
Tablets
- iPad Pro (3rd generation and later)
- iPad Air (3rd generation and later)
- iPad Mini (5th generation and later)
- iPad (7th generation and later)
- Surface Pro LTE models (selected models)
Smartwatches
Many cellular smartwatches use eSIM to stay online without a paired phone. Supported models include:
- Apple Watch Series 3 and later (GPS + Cellular)
- Samsung Galaxy Watch models with LTE
- Google Pixel Watch
Laptops
Several laptops with LTE or 5G options in the U.S. offer eSIM support, including:
- Microsoft Surface Pro with LTE
- Certain Lenovo ThinkPad models, including X1 and X12 Detachable
- Certain HP laptop models
How to get an eSIM data plan
There are several ways to get an eSIM plan, and most of them are fast and convenient. What you choose depends on your device, where you live, and whether you want something long-term or just enough data to get you through a trip.
Get an eSIM directly from your carrier
If you’re in the U.S., the major carriers all offer eSIM for compatible iPhones, Android phones, tablets, and wearables. And if you’re already a customer, you can usually convert your physical SIM to an eSIM right in the carrier’s app or account portal. New customers can activate an eSIM during setup or by scanning a QR code from the carrier, skipping the store visit.
Get a travel or secondary eSIM plan
If you’re headed abroad, dozens of third-party providers sell travel eSIMs you can install before you board your flight. These are perfect when you want local data without touching your main number.
Get an eSIM with ExpressVPN plans
ExpressVPN partners with eSIM provider holiday.com to offer a travel eSIM to subscribers on its Advanced and Pro plans. You can activate the eSIM online without a physical SIM card, and it offers coverage in more than 150 countries. When signing up, eligible users receive a coupon code that they can redeem on holiday.com.
Should you use a VPN with eSIM?
Yes, you should use a virtual private network (VPN) with an eSIM for the same reasons you’d use a VPN with a physical SIM.
An eSIM does not change how your internet connection works. Using an eSIM is functionally the same as using a removable SIM card. Once activated, your device connects to the mobile network and uses cellular (mobile) data (of course, you can also use Wi-Fi). Mobile data is generally harder to intercept than public Wi-Fi, and it doesn’t expose you to common public Wi-Fi risks like unsecured networks, evil twin (fake) hotspots, or local network snooping.
That said, “harder to intercept” doesn’t mean “private” or “fully protected.” An eSIM does not mask your IP address from websites you visit and doesn’t protect you from internet service provider (ISP)-level monitoring.
In other words, an eSIM provides connectivity, not privacy or anonymity.
Using a VPN on mobile data (whether via eSIM or physical SIM) therefore makes sense because a reputable VPN:
- Encrypts your internet traffic.
- Masks your IP address from websites.
- Limits what your ISP can see when you browse the internet.
Best practices for secure travel with eSIM and VPN
You can make travel a lot safer with a few simple habits:
- Turn on your VPN before joining any new Wi-Fi network.
- Use your eSIM’s mobile data when you can, since carrier networks are usually safer than open Wi-Fi.
- Avoid logging into sensitive accounts on unsecured networks.
- Update your device before you leave so you’ve got the latest security fixes.
- Turn off auto-join for unfamiliar Wi-Fi networks.
- Use strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for important accounts.
These steps go a long way in places like airports and hotels, where open networks are everywhere and you don’t know who else is connected.
FAQ: Common questions about eSIM
Is an eSIM better than a SIM?
For many users, yes. It’s easier to activate and easier to switch, and you never have to deal with a tiny plastic card that’s easily damaged or lost.
Does eSIM affect battery life?
Not really. eSIM and physical SIM technology use about the same amount of power. Your battery depends far more on things like signal strength and how much data your phone is using.
Can I use eSIM without internet?
You’ll need the internet to download and activate the eSIM. After that, it works just like a regular SIM and doesn’t need a connection.
What is an iSIM?
An iSIM is the next step in SIM tech. It’s built directly into the device’s main processor instead of being a separate chip. It saves space and is used in ultra-compact gadgets and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Does eSIM work internationally?
Yes, as long as your phone’s unlocked and your carrier or eSIM provider supports roaming or sells local travel plans. Many travel eSIMs can be set up instantly through a QR code or app.
Can I use multiple eSIMs on one device?
Yes, many modern phones can store several eSIM profiles. Some only let you keep one active, while others support two active eSIMs at the same time.
Can I use an eSIM and a physical SIM at the same time?
On many phones, yes. Dual SIM support lets you run both at once for calls, texts, and data.
Does an eSIM change your phone number?
No. Moving from a physical SIM to an eSIM doesn’t involve a change of phone number, unless you ask your carrier to change it.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN